Reverse logistics is a strategic and crucial process for growth and cost management in the eCommerce environment. The management of returns, transportation, and order traceability not only represents an additional cost, but also significantly impacts the quality of the customer experience.
As an online seller, understanding and managing reverse logistics is crucial to scaling your eCommerce operations efficiently. Key factors to consider include product type, return policies, transportation costs, and legal requirements. Using specialized eCommerce returns software can also help automate processes and streamline your strategy.
In this comprehensive guide, I delve into the elements that constitute reverse logistics in eCommerce, offering practical tips and the best strategies for its efficient management.
What is reverse logistics for eCommerce?
Reverse logistics is the strategic process of planning, implementing, and controlling the flow of returned products back to suppliers or distributors. It encompasses the procedures and systems involved in managing the reverse movements of goods in the supply chain.
Traditionally, reverse logistics has been associated with transportation and operational costs. However, its significance has grown over time, becoming a crucial factor in enhancing customer satisfaction and retaining revenue.
Difference between reverse logistics and traditional logistics
Reverse logistics and traditional logistics are distinct processes that handle the movement of goods but in opposite directions. Traditional logistics focuses on the forward movement of goods from suppliers to buyers, while reverse logistics manages the reverse flow, from buyers back to the original point of origin.
The impact of reverse logistics on eCommerce
Returns can be a significant cost for e-commerce businesses. According to a study by the National Retail Federation, returns in the United States represented 16.5% of online sales in 2022. This means that for every $1 billion in sales, a loss of $165 million was incurred in merchandise returns. In addition, return fraud represents a loss of $10.40 for every $100 in accepted returns.
Returns can also affect customers' perception of the company. Consumers who have a positive experience with returns are more likely to make future purchases. On the other hand, consumers who have a negative experience with returns are more likely to stop buying from the company.
In addition, consumers demand a simple and hassle-free return experience. A study by Nice found that 81% of consumers prefer to manage any interaction themselves, including product returns. This means that e-commerce businesses not only need to focus on optimizing reverse logistics to reduce costs, but it is also essential to add return portals so that customers can process their returns with maximum freedom.
Recommend to read
Unlock latest strategies and insights about return management by reading our comprehensive guide.
Benefits of automating eCommerce returns logistics
Enhanced customer experience and satisfaction. Customers who have a positive return experience are more inclined to patronize the same company repeatedly. Automating return logistics can assist e-commerce businesses in providing a quicker, simpler, and hassle-free return experience. This can contribute to boosting customer satisfaction and expanding sales.
Reduced logistics costs and incidents. Automating logistical procedures, such as return claims, refunds, and return analysis, can help e-commerce businesses conserve time and resources. This can result in a decrease in logistics costs, as well as a reduction in return-related incidents.
Reduced workload on the customer service department. An efficient return process can liberate customer service department personnel to concentrate on other tasks that are more valuable to the organization. This can contribute to enhancing employee productivity and satisfaction.
Sustainable supply chain. Automating return logistics can help e-commerce businesses lessen the environmental impact of their operations. For instance, automating return pickup can aid in reducing fuel consumption and greenhouse gas emissions.
Improved inventory management and reduced stockouts. Automating return logistics can aid e-commerce businesses in managing their inventory more effectively. This can contribute to minimizing stockouts, as businesses can promptly identify items that require restocking.
Increased total revenue. By utilizing a return management system like Outvio, e-commerce businesses can motivate their customers to exchange their returns for higher-value products. By facilitating a simplified exchange process, not only is lost revenue recouped, but it can also be raised.
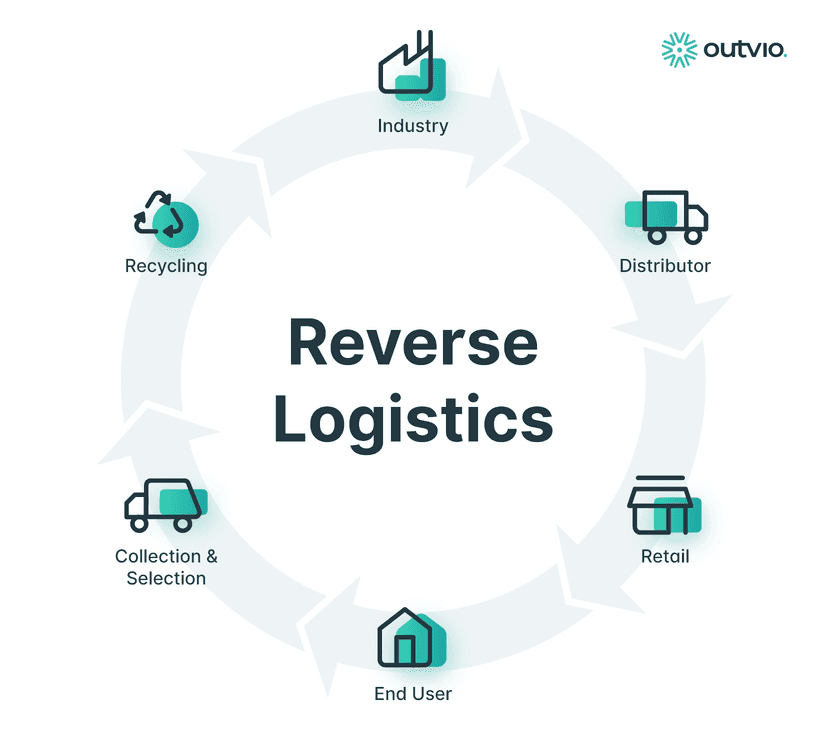
Logistics reverse process stages in eCommerce
Returns policy
While not technically part of reverse logistics, the returns policy significantly impacts the overall process. It establishes the guidelines that customers must adhere to when making a return.
These conditions encompass the following aspects:
- Refunds: Who will bear the return shipping costs? Will the entire purchase amount be refunded, including shipping fees? Will the purchase amount be refunded as store credit for future purchases?
- Pickups: Will customers handle product returns independently or will the eCommerce company arrange for pickup?
- Return Label: Will the eCommerce company provide customers with a return label?
- Deadlines: What is the maximum timeframe for making a return?
- Product Condition: Which items are eligible for return? Under what conditions must they be in order to be accepted?
Carrier management
Carriers play a crucial strategic role in reverse logistics strategies. They handle the collection of returned products, provide valuable insights for route optimization and strategic improvements, and assist businesses in meeting customer return requirements. Ultimately, the return experience depends on the efficiency and reliability of your transportation partners.
At this juncture, we face a crucial decision: What type of relationship do we want to establish with carriers? Several options are available:
- Outsource Entire Operations to a 3PL: This approach is the simplest, as the 3PL manages the entire process, from product pickup to return to the warehouse. However, it also entails the highest expenses.
- Invest in In-House Development to Integrate Carriers Directly into Your System: This option provides greater control over the process, but it necessitates a substantial investment in time and resources.
- Leverage Shipping Software with Pre-Integrated Carriers: This is the most suitable option for eCommerce businesses seeking effective reverse logistics without significant upfront investment. Additionally, return management software boasts specific features designed to enhance the customer's return experience.
The webservice
A web service is a software application that allows communication and data exchange between two computer systems. In the context of logistics, a web service allows communication between a company's computer systems and transportation systems.
It is essential to ensure proper synchronization between the company's web service and the transportation provider's web service. This is because the transfer of information and order monitoring depend on it.
A large part of logistics transportation incidents occur at this point in the process. Therefore, it is important for companies to conduct synchronization tests regularly to ensure proper operation.
Returns requests
Returns requests, also known as RMA authorizations, play a pivotal role in enabling sellers to effectively identify and manage product returns. They provide a comprehensive means of understanding the intricacies of the return and taking decisive steps for efficient handling.
Once approved, sellers should diligently oversee the return process and take the appropriate course of action, such as issuing a refund or providing a replacement.
Key Details of an RMA Request
- Customer Information: Name, address, phone number, email address, etc.
- Product Information: Order number, product number, date of purchase, etc.
- Return Reason: Defective item, incorrect item, change of mind, etc.
- Shipping Instructions: Return address, shipping method, etc.
E-commerce Return Request Submission Options
- Manual Contact with Customer Support Department: This method is not advisable due to potential delays and backlogs, which can significantly impact the customer experience.
- Utilize a Seamless Integrated Digital Portal: This approach empowers customers to manage their return requests independently, promoting efficiency and guaranteeing a prompt and effective response to their needs.
Return labels
A return label in e-commerce is a crucial document provided to the customer to streamline and facilitate the return process for a product. This label contains vital information that enables the return to be identified, tracked, and managed effectively. It is typically enclosed within the original package shipped to the customer or sent electronically.
The presence of a return label simplifies and streamlines the return process for both the consumer and the merchant. Some of the key elements that are typically included on a return label are:
- Sender Address: Clearly identifies the customer who initiated the return.
- Return Address: Indicates the precise location to which the product must be returned.
- Order Information: Provides detailed information about the transaction, such as the order number and a description of the items being returned.
- Return Authorization Number (RMA): Links the return to the approved return request issued by the merchant.
- Tracking Number: Enables real-time tracking of the package's movement throughout the return process.
Pickups
Logistics providers offer a diverse range of return pickup options, which is crucial as it significantly impacts the customer experience. It's advisable to provide various pickup options to cater to the diverse needs and preferences of your customers.
Here are some of the most common pickup types employed in the returns process:
- Home Pickup: Logistics providers schedule a pickup of the product at the customer's preferred address. This method proves convenient for customers who cannot physically transport the package to a drop-off location.
- Drop-Off: Customers can personally deliver the product to a pickup point designated by the logistics provider or merchant. This could be an affiliated store, a kiosk, or a dedicated drop-off location.
- Postal Return: Customers can mail the product back to the warehouse using conventional postal services. This method may appeal to individuals who prefer to manage the return process independently.
- Store Return: Some merchants allow customers to return products directly to a physical store affiliated with the merchant. This seamlessly combines the convenience of e-commerce with the accessibility of a brick-and-mortar establishment.
- Express Pickup: Specialized logistics providers offer rush pickup services for urgent returns, expediting the process for specific cases.
In addition to these common pickup options, some merchants may offer unique pickup services tailored to their specific customer base and operational capabilities. For instance, some retailers may partner with local couriers to provide same-day pickup services within specific areas.
Reconditioning, remanufacturing, and recycling
While some returns of brand new and unused products can be effortlessly integrated back into inventory, others may be redirected to a secondary market for reconditioning and resale.
It is crucial for businesses to have an efficient reverse logistics solution that meticulously guides each product return to the appropriate destination, employing automatic routing based on the product category and condition.
By establishing a well-structured returns management process, businesses can avert their returned products from ending up in landfills and guarantee the most environmentally conscious option for each product.
Reconditioning vs remanufacturing
Reconditioning and remanufacturing are two processes that restore used products to a functional state. However, there are significant distinctions between the two approaches.
Reconditioning
Reconditioning involves cleaning, repairing, and replacing faulty or damaged components of a product. The objective is to restore the product to a functional state, but not necessarily to its original factory condition.
Remanufacturing
Remanufacturing is a more profound and intricate process than reconditioning. It entails completely disassembling the product, inspecting it, and replacing all defective or worn-out components. The goal is to return the product to its original factory condition or even enhance its performance.
Product exchanges
Product exchanges, offered by some eCommerce as an alternative to returns, can be a mutually beneficial solution for both customers and store.
Customers can acquire the product they initially desired, while eCommerce can mitigate the expenses associated with product returns and subsequent resale. However, this option also presents challenges for merchants, which must establish clear processes for managing product exchange logistics and ensuring the seamless and accurate delivery of the replacement product requested by the customer.
To implement effective exchange strategies that drive revenue growth, should consider integrating automated software equipped with intelligent recommendations and real-time payment processing capabilities. Outvio is a potential solution that offers these features.

Common challenges in eCommerce reverse logistics
Customer experience issues
- High return rate. A high return rate can pose challenges for both customers and businesses. Excess product returns translate into additional costs and a poor customer experience, straining internal departments.
- Complex return process. A convoluted return process leads to customer frustration and increased administrative costs. Unclear forms or inadequate requirements can leave buyers dissatisfied and increase their reliance on customer service calls.
- Extended customer pickup wait times. Consumers demand prompt and convenient shipping, including free shipping and effortless returns. Delays in customer pickup can significantly impact the user experience and customer satisfaction.
Logistics management issues
- Product damage during returns. Product damage during the return process is a significant challenge in reverse logistics. Improper handling during transportation can not only affect product quality but also increase reverse logistics expenses.
- High transportation costs. Transportation expenses for returned items can be substantial. According to FreightWaves, the total cost of transporting a $50 item back to the origin can reach approximately 59% of the selling price. Effective transportation management is crucial for eCommerce businesses to reduce reverse logistics costs.
- Inadequate inventory management. Inefficient coordination can lead to product availability issues, inventory loss, and a reduced ability to meet demand.
- Lack of analytics and monitoring. Insufficient analysis and ongoing monitoring in reverse logistics can hinder understanding of return patterns and overall process efficiency.
4 Essential KPIs for eCommerce reverse logistics
Return rate
The return rate is a crucial metric that measures the percentage of products returned in relation to the total number of products sold. It serves as a valuable indicator of customer satisfaction and product quality. A high return rate can highlight potential issues such as products failing to meet customer expectations or a complicated return process causing unnecessary hassles.
The return rate can be evaluated at various levels, including product-level, product category-level, or store-level. Additionally, it can be analyzed across different time frames, such as monthly or annually.
Return processing time
The return processing time represents the duration it takes for a company to process a returned product, from the moment it is shipped by the customer to the issuance of the refund or credit. This metric directly impacts customer satisfaction and the overall efficiency of the return process. A prolonged return processing time can lead to customer frustration, potentially discouraging them from making future purchases from the same company.
The return processing time is calculated by counting the number of days between the shipping date of the returned product and the date the refund or credit is issued.
Return cost
The return processing cost encompasses the total expenses associated with handling a return, encompassing labor costs, material costs, and transportation costs. This metric serves as a significant indicator of the profitability of reverse logistics. A high return processing cost can erode a company's profits.
The return processing cost is determined by adding up all the expenses incurred during the return process.
Returning value
The returned value represents the monetary worth of the returned products. It serves as a key indicator of the profitability of reverse logistics. A high returned value can help offset the return processing costs and contribute to overall profitability.
The returned value is calculated by multiplying the number of returns by the average selling price of the returned products.
Tips to enhance return logistics
A perfect reverse logistics strategy is one that is profitable, efficient, and meets customer expectations. To design a perfect reverse logistics strategy, it is important to follow these steps:
1. Understand your starting point
Before you invest in optimizing your reverse logistics, it is important to determine the scope of your current logistics and take into account your future sales forecasts. To do this, analyze your processes, your resources, and your capabilities. This information will help you identify areas that need a boost and what strategy or technology they require.
2. Define your goals
Once you have a clear understanding of your current situation, it is time to define your goals for reverse logistics. Do you want to reduce costs? Improve customer satisfaction? Recover more value from returned products? Once you have your goals clear, you can develop a strategy that will help you achieve them.
3. Select the right technology
Technology can help you automate tasks, improve efficiency, and reduce costs. There is a wide range of technological solutions available for reverse logistics, so it is important to compare the different options to find the one that best suits your needs.
4. Implement the strategy
Once you have developed your strategy, it is time to implement it. This will involve communicating the changes to your team and your customers, as well as providing them with the training and resources they need to implement the new strategy.
5. Measure performance
It is important to measure the performance of your reverse logistics strategy to ensure it is achieving its goals. This will help you identify areas where you can make improvements.
7. Key points for a perfect reverse logistics strategy
Here are some key points to keep in mind when designing a perfect reverse logistics strategy:
- Offer a simple and hassle-free return experience for your customers. This is essential for maintaining customer satisfaction and reducing the risk of customers churning.
- Choose the right return method for your customers. Some customers may prefer to mail returns, while others may prefer to return them in-store. Offering a variety of return options will help you meet the needs of all your customers.
- Process returns quickly and efficiently. Customers expect to receive their refunds or credits as soon as possible. Implement an efficient return processing process so you can meet these expectations.
- Recover the maximum value of returned products. If returned products are in good condition, you can sell them as refurbished products. If products are damaged or defective, you can recycle them or donate them to charities.
8. Technological solutions for reverse logistics
There is a wide range of technological solutions available for reverse logistics. These solutions can help you automate tasks, improve efficiency, and reduce costs.
Some examples of technological solutions for reverse logistics include:
Conclusion
In recent years, returns have played an increasingly significant role in consumer shopping behavior. While they were once regarded solely as an operational cost factor, they have now become indispensable for delivering an exceptional customer experience.
Inefficient reverse logistics operations not only lead to an inexorable decline in expenditures and profit margins but also tarnish the final impression of your eCommerce brand for your users. The truth is, an inconvenient return management process can be far more detrimental than a return itself, driving many customers away from returning to your business.
To optimize your reverse logistics operations, diligently implement the practices outlined in this guide: thoroughly analyze your current processes, establish clear and efficient protocols, and always prioritize your customers at the heart of your strategy. By adopting these measures, you can enhance customer satisfaction, reduce costs, and ultimately strengthen your eCommerce brand.