SEO is one of the most profitable strategies to ensure the success of your eCommerce. However, search engine optimization requires two essential elements: patience and professional knowledge.
To stand out from your competitors, you will need to apply more than just basic theory. In this article, you will find the best practices that professional SEOs use in the eCommerce industry.

1. SEO best practice for eCommerce: finding the search intent
Keywords are the terms that your customers will use to find you. They serve as a gateway for users who have never heard of you to end up in your business. The goal of a SEO strategy is to associate each keyword with an eCommerce URL: it must be perfectly chosen from the start.
There are two types of keywords that you should work on in parallel:
- Long-tail: they have a higher search volume and higher competition. They are usually used for the Home page and the main categories.
- Short-tail: the number of searches and the competition is lower, so they are easier to rank. They are usually used for subcategories, product sheets, or blog posts.
To find keywords, you can use tools like Ahrefs, Semrush, the Google Ads planner, or Google autocomplete. You can also analyze the keywords positioned by your competition. This is incredibly useful for knowing how to find positioning opportunities.
What is search intent?
It is the purpose that a user has when making a query in a search engine. Knowing the search intent is important to create relevant and interesting content for the user.
Normally, we divide the search intent into three categories:
- Informational: the user is looking for information about a specific topic.
- Transactional: The user wants to purchase a product or service.
- Mixed: a combination of the two above.
To know the search intent, it is as simple as analyzing the results that Google offers to a query. For example, if the word "blue shoes" appears in many product sheets, we would be facing a transactional keyword.
Best practices to conduct a keyword research for your SEO eCommerce strategy:
- Identify your competitors and analyze their strategies.
- Make a list of relevant keywords for your business and products. Include general and specific terms.
- Find a balance between keywords with high search volume and manageable competition.
- Group keywords into categories related to your products or services. Prioritize categories according to their importance to your business.
- Identify keywords that suggest a buying intent, such as "buy," "offer," "discount," etc. for your product sheets.
- Search patterns change, so review and update your keyword list periodically.
Once you have identified your keyword bank, you will need to add them in an orderly manner to an Excel sheet. The most advisable thing is to create a column for the URL, another for the keyword, another for the volume, and another for the search intent. Here is an example:
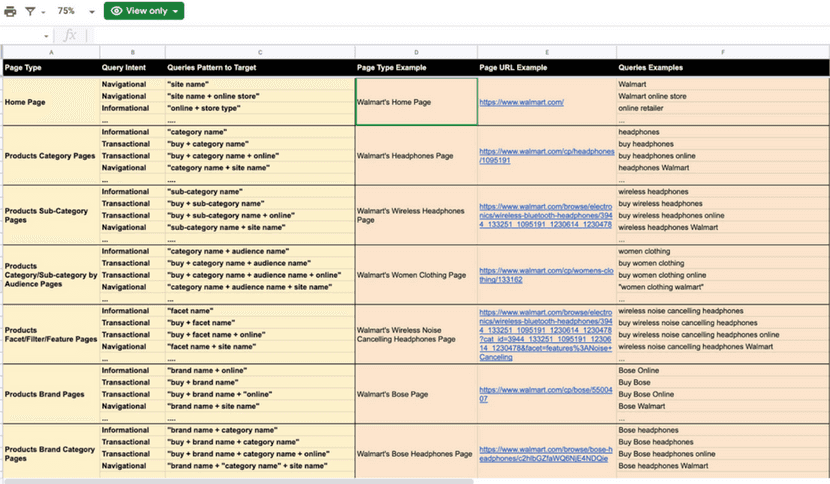
In this link, you will find two keyword mapping templates for eCommerce.
2. Web architecture clustering
Web architecture is the logical structure or sequence of URLs that make up a website and its navigation.
It is important that the structure is designed hierarchically and with a 1:1 formula (one URL, one keyword).
This is essential for several reasons:
- Helps Googlebot crawl and index your website pages
- Avoids orphaned pages
- Guides the customer through the conversion funnel
What is clustering?
A cluster is a method of organizing information. Its goal is to group similar or related content within a theme or category.
In the context of SEO for eCommerce, clustering is typically used to group product categories based on their relevance, popularity, and purchase intent.
For example, an online clothing store could group its product categories by season (winter, summer, spring, fall), gender (men, women, children), or type of garment (dresses, pants, shirts, etc.).
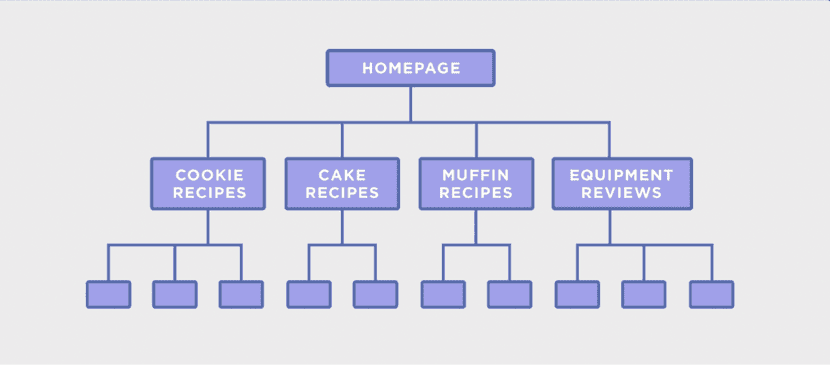
How to Approach Clustering
The ultimate goal is to use all the keywords from our previous study to create vertical categories that respond to the same search intent and the same semantic root.
Factors to Consider:
- Make sure the grouping makes sense from the user's perspective and is related to search needs.
- Reflect the structure of your clusters in the architecture of your site. In other words, a main page should link to a lower-priority subpage.
- The links between pages should be logical and accessible to promote navigation.
- Optimize URLs to their assigned keyword (we'll see this later).
- Distinguish between evergreen content (always relevant) and temporary content (offers, promotions). Create specific clusters for products or seasonal content.
Pro Tip: Use a tagging system to link all the products in a category horizontally and use secondary keywords to work on the semantics of that section. For example, you can unite all products from a section of sports shoes with an anchor text that says "sports footwear.
The five-click rule
This rule states that users should be able to find the information they are looking for with a maximum of five clicks or page jumps. In the context of eCommerce SEO, this means that product categories should be well-structured and organized so that users can find what they are looking for quickly.
3. Best practices for SEO on-page in eCommerce
On-page SEO is a series of practices that will help you increase the visibility of your eCommerce store in search engines.
In essence, it consists of optimizing each URL for the keyword that you assign it in your initial study, always taking into account the user's search intent.
3 best practices for SEO on-page in eCommerce::
1. Meta title and meta description optimization
These elements determine the text that the user sees when they perform their search.
In addition to including the keyword or secondary keywords, it is also advisable to add elements that arouse the user's curiosity or include product benefits. This helps to improve CTR, or the amount of clicks per impression.
Keep in mind that the title and meta description must be adapted to the search intent. It is not the same to address someone who wants to buy an item as it is to someone who only needs information.
Example:
Some eCommerce businesses use templates to create meta descriptions and meta titles in bulk to save time. This practice has some risk, as Google could consider it duplicate content.
Image optimization
Image management is quite important in eCommerce, as they are part of the product sheet. A high-quality image can lead to a sale. In addition, you can also optimize them to appear in Google's "Images" section.
Recommended practices:
- Include a descriptive text with a keyword in the ALT attribute. This will help the search engine understand the content of the image
- Reduce the size and weight of the image to improve web loading
- Make sure the image adapts well to the mobile version of your website
- Upload the images to your web manager with a friendly name, like a URL
SEO optimization for product and home page: best practices
The best practices to improve SEO on the home page and product pages of an eCommerce are:
1. Add relevant keywords
The first key to optimizing product pages for SEO is to add relevant keywords. These keywords should be extracted from your initial research. You should also avoid overusing them, as this is a practice penalized by Google: keyword stuffing. Add them naturally within the body of the text.
2. Write detailed and persuasive descriptions
Product page descriptions should be detailed and persuasive. They explain to users what the product is, its features, and benefits. To write quality descriptions, use clear and concise language.
3. Use headers and formatting
Headers and formatting help to organize the information on the product page in a clear and structured way. This makes it easier to read for both users and search engines.
Use headers to divide the information into sections. You can also use lists, images, and videos to improve the presentation of the information.
4. Encourage customer reviews
Customer reviews are a great way to generate trust and credibility. They also help to reduce bounce rate, a very important ranking factor for eCommerce SEO.
To encourage customer reviews, you can offer incentives, such as discounts or gifts. You can also send reminders to customers who have purchased a product to leave a review.
The Outvio Review Booster functionality will help you get positive customer reviews automatically and without any effort.
4. Best practices for SEO off-page in eCommerce
Domain authority is an important ranking factor. It is achieved through external links from other websites, which can be obtained through collaborations, organically, or for a fee.
However, not all backlinks will help you improve your visibility or domain authority. Some can even be harmful to your store.
Professional SEO off-page tips for eCommerce
- When you are going to invest in links for your eCommerce, try to avoid those with the rel="nofollow"; rel="ugc"; rel="sponsored" tags, as they will not add value to your strategy
- Look for links from domains with a higher authority than yours
- The text or anchor text that links to your content should contain your URL keyword and be as high up as possible on the page that gives it to you
- The page that provides the link should be about similar content to yours. Google will better understand the semantics of the content and, therefore, the theme of your page.
- A common mistake is to invest in links with high authority but low trust-flow or from a unrelated topic. It is important to take care of both metrics
- Review the frequency of link acquisition. If you receive too many links suddenly, Google will suspect that you are using unnatural practices
Tips for getting free links
- Analyze a competitor's website and see what backlinks they have lost and where they came from. You can then reach out to these websites and ask them to include your link to replace your competitor's link.
- Look to see if any websites that you would be interested in receiving a backlink from are linking to a broken or 404 link. You can then reach out to them and ask if they would be willing to replace that URL with one of yours.
- Create high-quality content that people will want to link to. This could include blog posts, articles, infographics, or videos
- Participate in industry forums and communities. This is a great way to connect with other people in your field and build relationships
- Guest blog on other websites. This is a great way to get exposure to a new audience
- Submit your website to directories and search engines. This will help people find your website when they are searching for products or services related to your business
5. Broken link maintenance
Broken links are links that point to pages that no longer exist.
They can occur for a variety of reasons, such as the deletion of a page, a change in URL, or a typo.
These links have a very negative impact on the SEO strategy of any eCommerce:
- Reduce authority. Google will not be able to crawl the content that other authoritative links point to.
- Degrade user experience. It is very frustrating to click on a link and end up on a page with an error code. It also reflects a lack of professionalism.
- Cause crawling issues. Search engine crawlers that find broken links are slowed down, making it difficult to index your content.
It is important to find and fix broken links as soon as possible. To do this, you can use a web auditing tool like Screaming Frog or Ahrefs. Once you have identified the broken links, you can take steps to fix them.
The best practices for fixing broken links and improve your eCommerce SEO strategy:
- Redirect the broken link to an existing page. This is the most common option. You can use a 301 redirect to redirect the broken link to a page that exists.
- Remove the broken link. If the page that the broken link pointed to is no longer relevant, you can remove the link.
- Update the link URL. If the page that the broken link pointed to has changed URL, you can update the link URL.
6. The Crawl Budget and the robots.txt Tag
The crawl budget is the amount of resources that Google dedicates to crawling and indexing a website. This budget is limited, so it's important to optimize and prioritize important pages. To do this, we need to use the robots.txt tag.
The robots.txt tag tells the search engine which pages we want to be crawled and which not. Additionally, we can add certain directives to guide the search engine and adapt it to the needs of our online store.
What directives can we add to a robots.txt tag?
- User Agent: specifies the search engine crawler to which the directives apply
- Disallow: tells the crawler not to crawl certain pages or domains of the website
- Allow: allows search engine crawlers to access specific pages or directories of the website that could be blocked by a Disallow directive
- Crawl Delay: specifies the time (in seconds) that search engine crawlers should wait between requests
- Sitemap XML: provides a sitemap of all the URLs that the robot should crawl
When working on eCommerce SEO, it is most common to use the Disallow directive to prevent the crawling of irrelevant URLs or that could lead to duplicate content. The most important ones are:
Disallow: /checkout/
Disallow: /cart/
Disallow: /account/
Disallow: /login/
Disallow: /register/
Disallow: /forgot-password/
Disallow: /reset-password/
Disallow: /*add-to-cart
How to check your Robots.txt file
To check if your Robots.txt file is properly configured, open a web browser and enter your domain name followed by "/robots.txt". For example, if your domain name is "www.example.com", you would enter the following URL:

If the file is properly configured, you should see a text file with a list of instructions for web crawlers. The file may contain instructions to allow or disallow crawling of specific pages or directories on your website.
Here is an example of a Robots.txt file:

This file allows all web crawlers to access all pages on the website.
If you see any errors or warnings in your Robots.txt file, you should correct them as soon as possible. Incorrect or outdated Robots.txt files can prevent web crawlers from indexing your website properly, which can impact your website's search engine ranking.
7. Avoiding duplicate content with the canonical tag
When you have multiple versions of the same product (sizes, colors, etc.), Google may consider that content as duplicate.
In these cases, we can use the canonical tag to tell the search engine which page to prioritize when indexing a piece of content.
Typically, an eCommerce store will set the most representative product variants with the highest conversion rates as canonical.
You can add the canonical tag to the <head> section of the HTML code for each variant page in question. Let's take a look at an example.
Suppose you have two variants of a t-shirt, one green and one blue. You decide that the blue variant is the canonical page.
In this case:
- The canonical page URL ("URL_of_the_blue_product_page") would be the full address of the blue t-shirt page
- Both variant pages (green and blue) have the same canonical tag, indicating that the blue version is the main or canonical version
Here's how to add the canonical tag to your website
- Open the HTML code for the page you want to set as canonical
- In the <head> section, add the following code
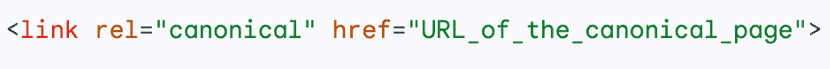
- Replace "URL_of_the_canonical_page" with the full address of the canonical page
- Save your changes
8. Add structured data
Structured data is a set of tags that are added to the code of a web page to provide additional information to search engines.
When you include structured data, it increases the chances that Google will show your products directly in the SERP. This is especially important in e-commerce, as it is a very efficient way to generate revenue.
These are the best practices for working structured data into your eCommerce SEO strategy:
Tips for adding structured data
Identify your structured data types: Determine which type of structured data is most relevant for your e-commerce site. Some common types include:
- Schema.org markup: You can use Schema.org markup to describe products, reviews, organizations, etc.
- Open Graph Protocol: Specific to Facebook, but also used by other services. You can use it to define properties such as title, description, image, etc.
- JSON-LD (JavaScript Object Notation for Linked Data): A structured data format that integrates well with JavaScript and is easy to implement.
Implementation
- HTML tags: Add the directive directly to the HTML code of your pages. For example, for products, you can use itemtype and itemprop to specify the type and properties of the item.
- JSON-LD: Puedes incluir el marcado JSON-LD en el <head> de tu página. Este es un ejemplo simple para un producto:

Testing and validation
Use structured data testing and validation tools, such as Google's Structured Data Testing Tool or JSON-LD Playground, to ensure that the markup has been implemented correctly.
Submit your data to Google Merchant Center
To avoid a potential conflict between price and stock data (one of the most common causes of synchronization problems), you can ask Google Merchant Center to automatically update the copy of your product data based on your website content when there is a discrepancy.
9. Increase Your Online Store's Speed
Improving the web loading speed of your online store is crucial for optimizing SEO and providing a better user experience. Here are some strategies to increase your loading speed:
Tips for improving online store load times:
- Compress your images. You can use formats like WebP
- Minify and combine CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files to reduce file size. Remove comments, whitespace, and unnecessary lines of code
- Use techniques like the "critical rendering path" to load visible content first and improve perceived speed
- Minimize the use of redirects, as each one adds additional loading time
- Configure browser caching to reduce loading time on subsequent visits
- Choose a reliable hosting provider that offers a fast and reliable connection
- Use a content delivery network (CDN) to cache your site's static content closer to your visitors
- Keep your software up to date, including your store platform, plugins, and themes
10. Best practices for international SEO in eCommerce
Hreflang is an HTML attribute used by search engines to identify different language versions of the same page.
You should use this tag whenever you have multiple pages in different languages that could be confusing. This will help your web pages to be indexed and displayed correctly.
For example, if you have sections of your website for a French audience, for example, an hreflang tag helps Google understand that the section should appear in the search results of Google.fr, not Google.com.
How to use the hreflang tag?
- Identify the relevant pages in multiple languages that could be confused by Google search.
- Determine the language in which you want each page to appear.
- Add the tag to the HTML code.
Here is an example of an hreflang tag:

This tag tells Google that the page at https://example.com/ should also be indexed for the Spanish language.
Best practices for using hreflang tags in your SEO strategy
- Use hreflang tags on all pages that have relevant content in multiple languages
- Use the correct language code for each language
- Use the href attribute to specify the URL of the page in the other language
- Place the hreflang tags in the <head> section of your HTML code
11. Explore alternative strategies to boost your business
In an increasingly competitive market, it is essential for eCommerce businesses to find alternative strategies to drive growth beyond organic search engine optimization.
In this regard, the order and delivery phases offer valuable opportunities to generate sales and improve the customer experience.
The order phase is a key moment in the purchase process, as it is when the customer makes the final decision to purchase the product or service. Therefore, it is important to take advantage of this moment to generate additional sales.
With Outvio, you can transform shipping, delivery, and returns processes into powerful recurring revenue channels. Thanks to its segmentation system and personalization capabilities, you can add relevant promotions to every customer interaction, among many other alternative strategies.




